Eliminate Food Waste in
Victoria’s Agriculture

- Reducing Food Waste: Streamlining processes to minimize food loss.
- Supporting Farmers: Providing resources and technology to increase efficiency and reduce waste.
- Improving Supply Chain: Optimizing the journey of crops from the farm to the table.

Wheat
Australia is one of the world’s largest wheat producers. Most wheat is grown in the grain belt, which spans southern Australia.

Barley
Grown mainly in Western Australia and South Australia, barley is used for food products and as animal feed.
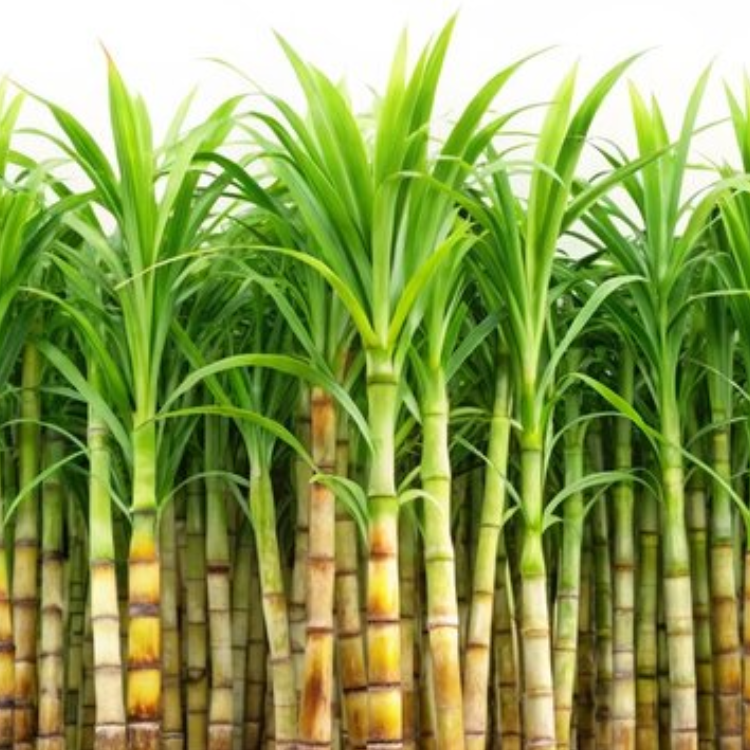

Sugar Cane
Grown in the tropical climates of Queensland and New South Wales.
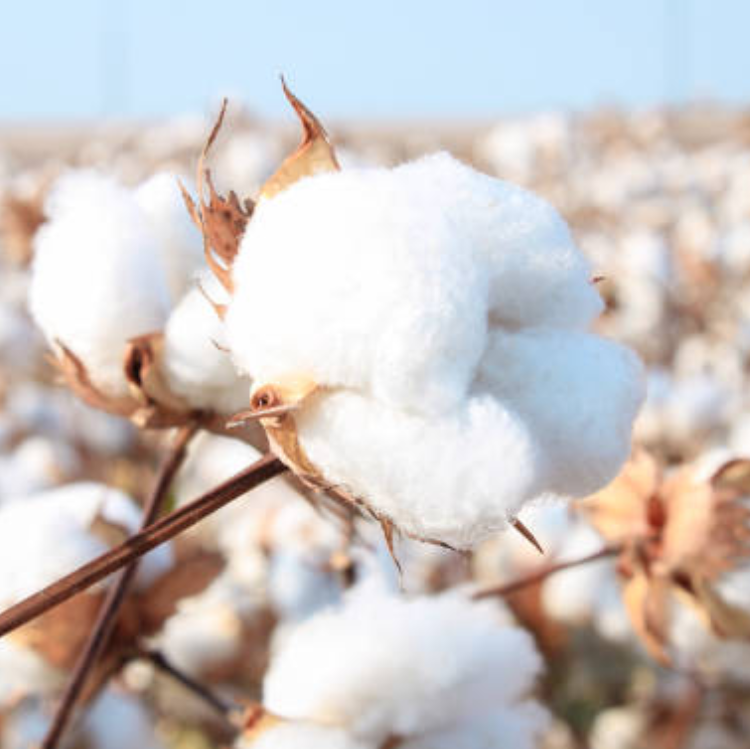

Cotton
Australia is a significant producer of cotton, especially in New South Wales and Queensland.
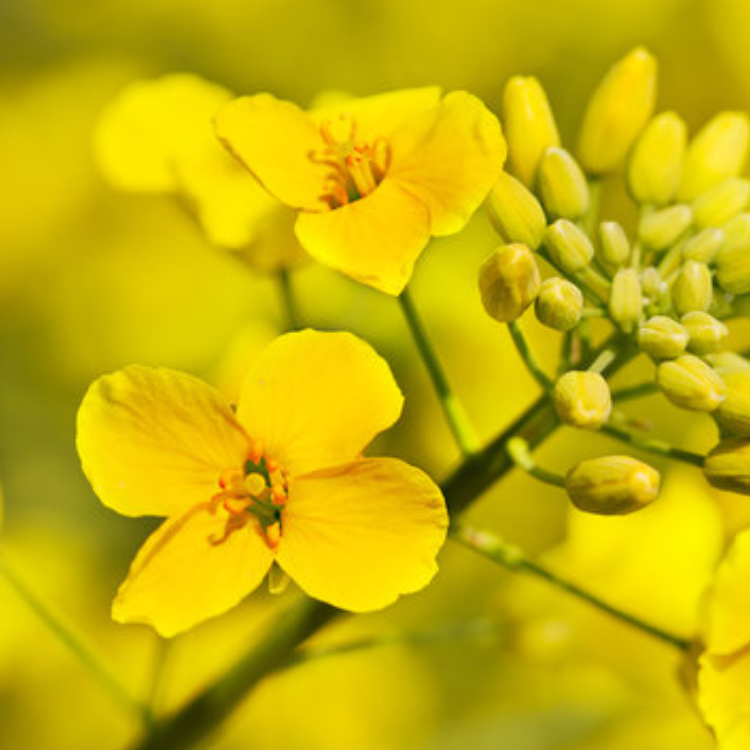

Canola
Grown mainly in Western Australia, South Australia, and Victoria.
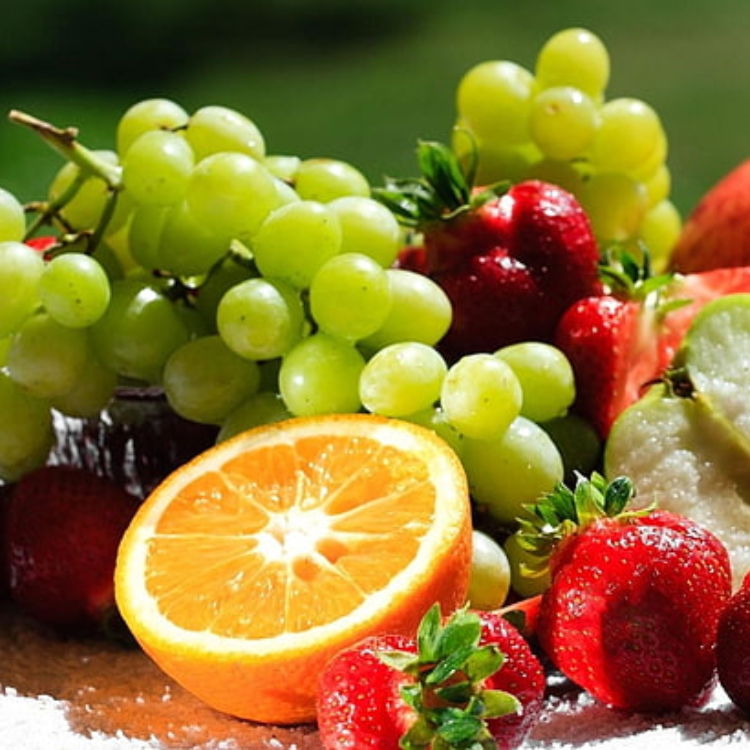

Fruit (Citrus, Apples, Grapes)
Grown in various parts of the country with major fruit-growing regions like the Riverina, Swan Hill, and the Adelaide Hills.
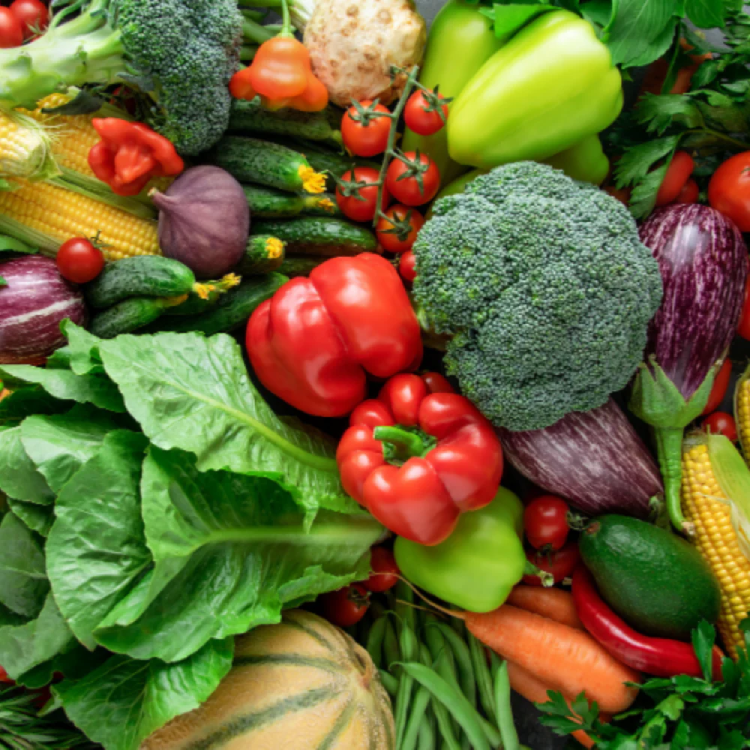

Vegetables
A range of vegetables are grown in Australia including potatoes, tomatoes, carrots, and onions.
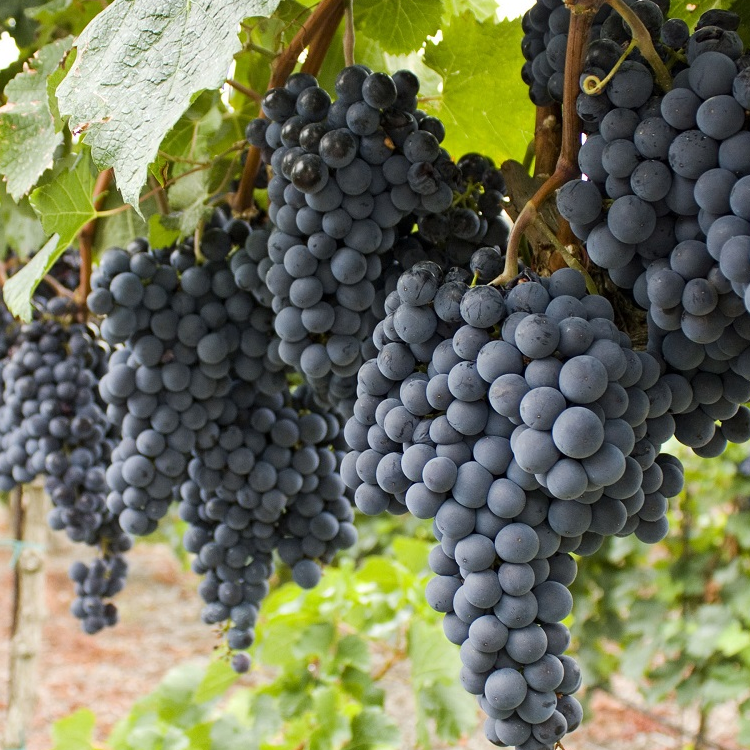

Wine Grapes
Australia's wine regions, such as the Barossa Valley, produce some of the best wines in the world.
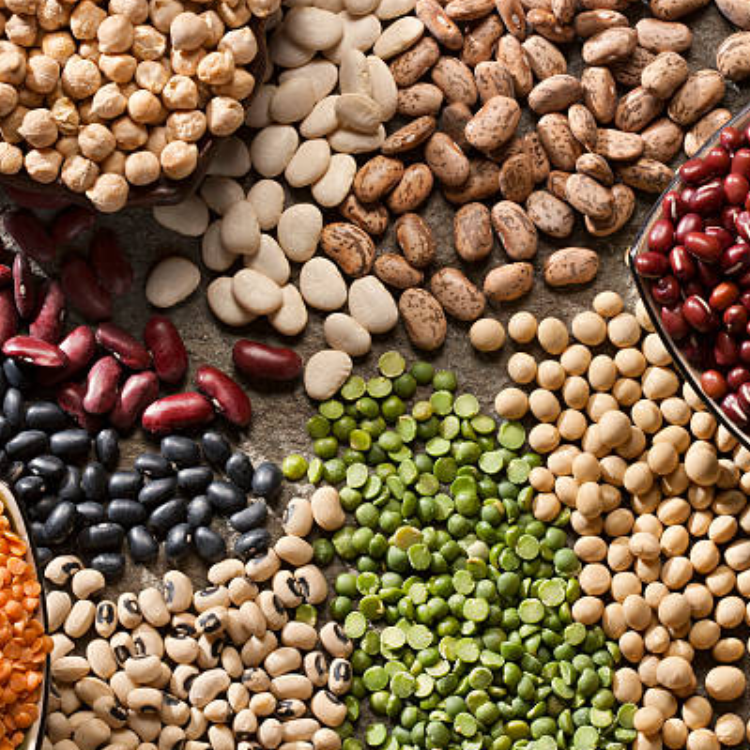

Chickpeas and Lentils
These pulse crops are a growing export commodity, particularly from regions like New South Wales and South Australia.
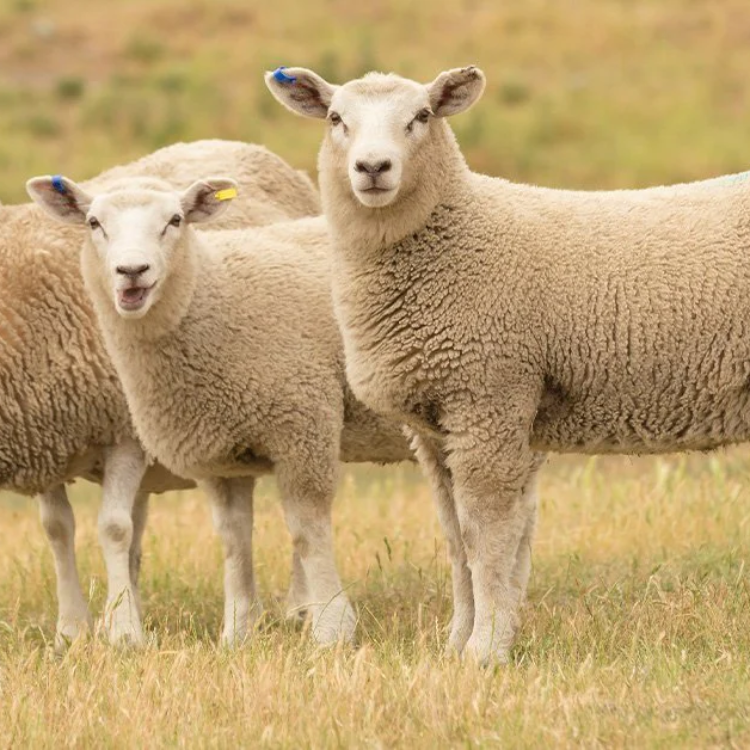

Livestock
While not a crop, livestock farming is equally important, with cattle, sheep, and poultry being raised for both domestic consumption and export.
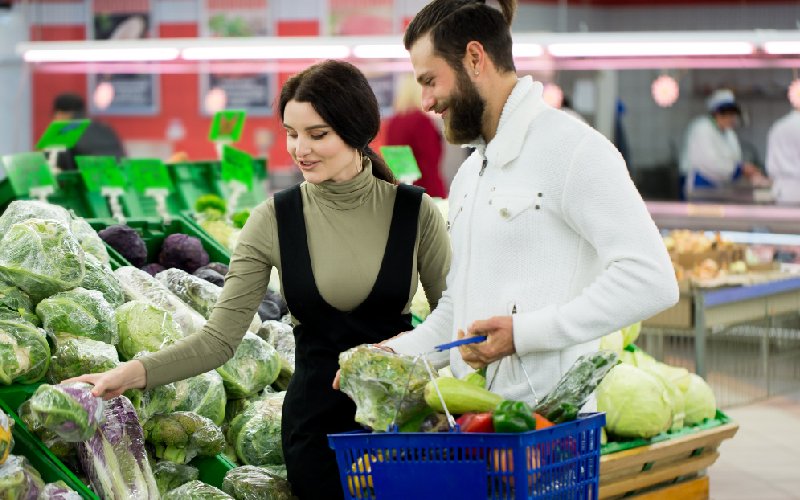

Farm-to-Consumer Direct Sales
By cutting out middlemen, farmers can sell directly to buyers and reduce food waste.
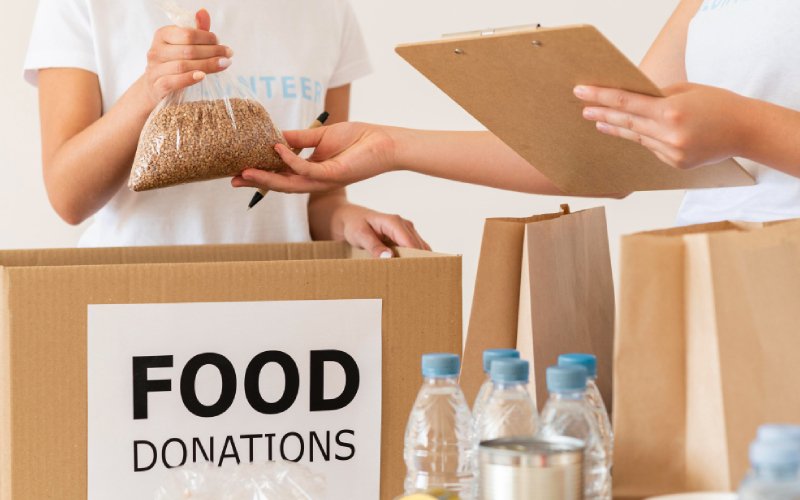

Food Donation Networks
Surplus food is donated to food banks and charities, ensuring it doesn’t go to waste.
Production
Farmers cultivate a wide range of crops across various regions, utilizing advanced agricultural practices to maximize yield and quality.
Processing
After harvest, crops are transported to processing facilities where they are cleaned, packaged, and prepared for distribution.
Food Waste Reduction Target
Economic Impact of Food Waste
Resilience in Agriculture
Increasing Crop Yields:
Farmers use modern agricultural practices like genetically modified seeds, advanced irrigation, and fertilization techniques to increase crop yields. Improved technology ensures that the same amount of land can produce more food, which helps feed more people.
Diversifying Crop Production
Farmers plant a variety of crops to meet diverse nutritional needs and reduce dependency on a single type of food. This includes growing grains, vegetables, fruits, and pulses like wheat, barley, chickpeas, and lentils alongside livestock.
Sustainable Farming Practices:
Farmers focus on sustainable practices, such as crop rotation and organic farming, to maintain soil health and reduce the environmental impact of food production. These practices help preserve the land for future generations while maintaining high food production levels.
Adoption of Technology
Drones, AI, and sensors are used to monitor crop health, manage resources efficiently, and forecast weather patterns. This helps farmers make informed decisions that boost crop productivity. Automated machinery and robotics in the field also reduce the labor needed and improve efficiency.
Managing Supply Chain & Logistics
Farmers use advanced storage and transportation systems to ensure that food is distributed efficiently, minimizing waste and ensuring fresh produce reaches consumers. Cold storage facilities and transport networks are key in reducing spoilage, especially for perishable items like fruits and vegetables.
Improved Water Management
Efficient water management systems like drip irrigation help farmers use water more effectively, especially in areas where water resources are limited. Conservation efforts ensure a consistent water supply for irrigation, vital for crop production.
Local Farming and Urban Agriculture
Urban farming and local agriculture have gained popularity, reducing the distance between farms and cities and ensuring fresh food availability. Farmers in urban areas are cultivating vegetables, herbs, and even fish to meet local demand.
Food Waste Reduction
Farmers work on improving food preservation methods and reducing food waste. This ensures that the food produced is used efficiently and not wasted. Partnerships with food banks and charities help in distributing excess food to those in need.
Government Support and Policies
Government policies and subsidies often support farmers in scaling production and adopting new technologies. These policies ensure that farmers remain economically viable and can continue producing enough food for the population.
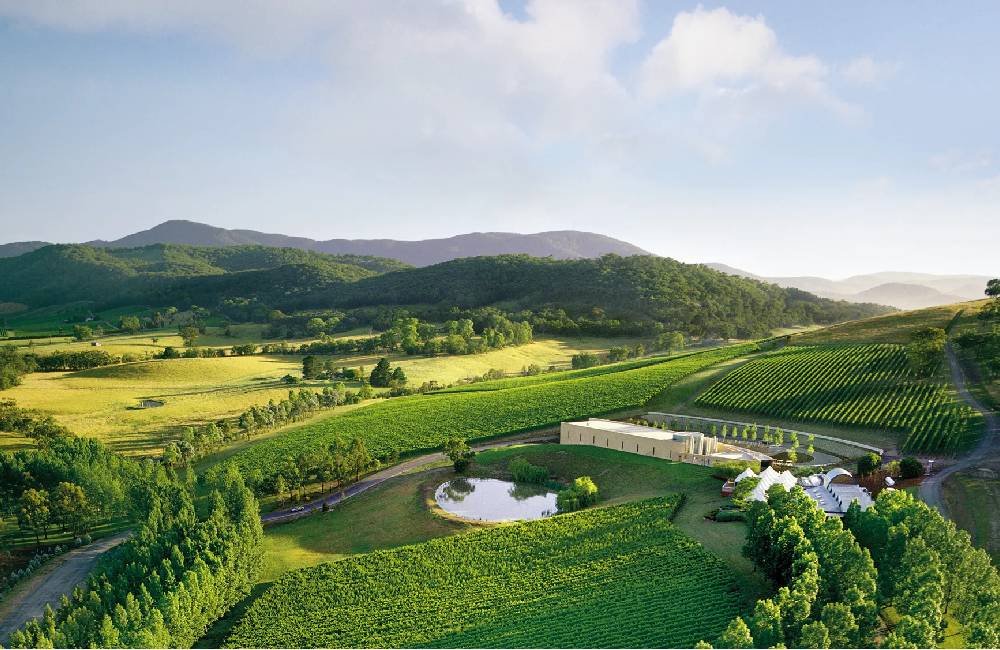


Crops: Wine grapes, apples, berries, and vegetables.
Description: The Yarra Valley is a renowned wine-producing region. It’s also known for high-quality apples and berries. The region's cool climate is ideal for these crops.
Crops: Fruit (particularly stone fruits such as peaches and nectarines), vegetables (including onions and carrots), and dairy.
Description: Shepparton is one of Australia's largest food-producing areas. It is often referred to as the "Food Bowl" of Victoria due to its fertile soils and irrigation systems.


Crops: Potatoes, vegetables, and dairy.
Description: Known for potato farming, this region also produces vegetables and dairy products. The coastal climate supports crops like potatoes, onions, and tomatoes.
Crops: Seafood (fishing) and vegetables. (including onions and carrots), and dairy.
Description: Located on the coast, this region is famous for seafood production, especially prawns, and also produces some local vegetables.


Crops: Dairy, vegetables, and beef cattle.
Description: Gippsland is a major dairy-producing region in Victoria. It also grows vegetables like potatoes, cabbage, and cauliflower, and has large-scale beef and lamb production.
Crops:Fruit trees (apples, pears), and some vegetables.
Description: Warburton is located in the Yarra Ranges and is known for its apple and pear orchards. The cool climate is perfect for these fruit crops.


Crops:Dairy and beef cattle.
Description: The region near the Twelve Apostles is home to grazing land used for beef and dairy production. The natural environment supports large herds of cattle.
Crops:Wine grapes, olives, and grazing land for sheep and cattle.
Description: The Grampians region has a unique climate that supports vineyards and olive groves. Sheep and cattle grazing also occurs throughout the area.


Crops:Limited due to the mountainous terrain, but small-scale orchards and livestock (sheep, alpacas).
Description: The Alpine region is known for its rugged terrain and harsh winters, which limits crop production. However, small-scale farming operations include orchards and livestock grazing.
Crops:Limited crop production; mainly livestock grazing (sheep and cattle).
Description: These high-altitude regions are primarily known for grazing sheep and cattle due to their mountainous landscapes.


Crops:Wine grapes, apples, and berries..
Description: Located in the Yarra Valley, Healesville is known for its wine production, as well as its apple and berry farming.
Crops: Orchards (apples, berries), vegetables, and flowers.
Description: The Dandenong Ranges is home to fruit and vegetable farming, as well as flower growing. The climate supports the cultivation of apples, berries, and a variety of ornamental plants.

there’s a way for you to make a difference. Here are some ways you can help:
Post your available crops, hire workers, and reduce waste.
Pre-order crops, support local farmers, and donate to food banks.
Join our network to buy crops directly from farmers and reduce waste in your supply chain.
Help distribute surplus food to those in need.
Stop Food Waste in Victoria!

our community loves Us





